- 131.00 KB
- 2022-06-17 15:50:42 发布
- 1、本文档共5页,可阅读全部内容。
- 2、本文档内容版权归属内容提供方,所产生的收益全部归内容提供方所有。如果您对本文有版权争议,可选择认领,认领后既往收益都归您。
- 3、本文档由用户上传,本站不保证质量和数量令人满意,可能有诸多瑕疵,付费之前,请仔细先通过免费阅读内容等途径辨别内容交易风险。如存在严重挂羊头卖狗肉之情形,可联系本站下载客服投诉处理。
- 文档侵权举报电话:19940600175。
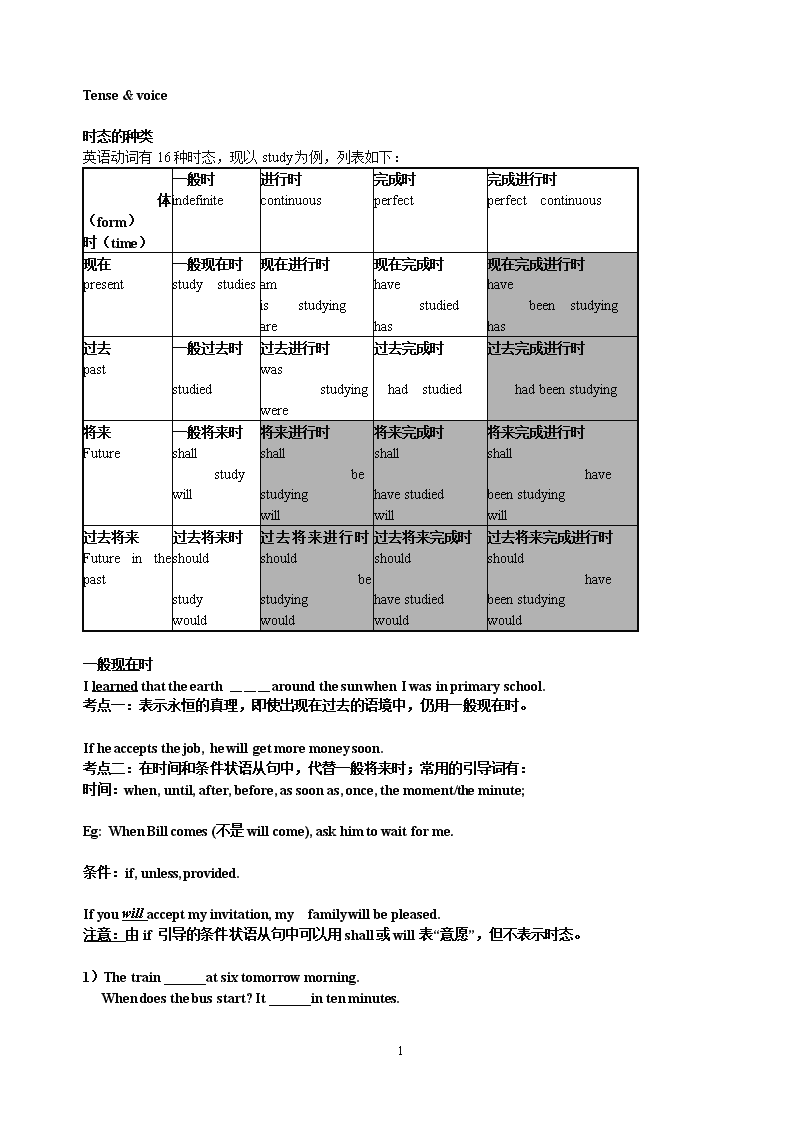
Tense&voice时态的种类英语动词有16种时态,现以study为例,列表如下: 体(form)时(time)一般时indefinite进行时continuous完成时perfect完成进行时perfect continuous现在present一般现在时study studies现在进行时amis studyingare现在完成时have studied has 现在完成进行时have been studyinghas过去past一般过去时studied过去进行时was studyingwere过去完成时 had studied过去完成进行时 hadbeenstudying将来Future一般将来时shall studywill将来进行时shallbestudyingwill将来完成时shallhavestudiedwill将来完成进行时shallhavebeenstudyingwill过去将来Futureinthepast过去将来时shouldstudywould过去将来进行时shouldbestudyingwould过去将来完成时shouldhavestudiedwould过去将来完成进行时shouldhavebeenstudyingwould一般现在时Ilearnedthattheearth___aroundthesunwhenIwasinprimaryschool.考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。Ifheacceptsthejob,hewillgetmoremoneysoon.考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when,until,after,before,assoonas,once,themoment/theminute; Eg:WhenBillcomes(不是willcome),askhimtowaitforme.条件:if,unless,provided.Ifyouwillacceptmyinvitation,myfamilywillbepleased.注意:由if引导的条件状语从句中可以用shall或will表“意愿”,但不表示时态。1)Thetrain______atsixtomorrowmorning. Whendoesthebusstart?It______intenminutes.12
考点三:下列动词:come,go,arrive,leave,start,begin,return,open,close的一般现在时表将来。这主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。2)倒装句(由here,there开头的句子,动词用一般 现在时表示现在正在发生的动作) Herecomesthebus.=Thebusiscoming. Theregoesthebell.=Thebellisringing.现在进行时Thehouseis_____________thesedays.Thelittleboyisalwaysmakingtrouble.考点一:与频率副词,如always,constantly,continually等连用表示说话人的某种感情色彩(赞叹、厌烦、埋怨等)。Heisalwaysthinkingofhiswork(赞许)他老是把东西乱扔。Heisconstantlyleavinghisthingsabout.(不满)他老爱说大话。Heisalwaysboasting(厌烦)考点二: 表示在最近按计划或安排要进行的动作,仅限于少量动词:go,come,leave,start,arrive,return,stay,do,have,seesboff…Areyoustayingheretillnextweek?工作进行的怎么样?Howareyougettingonwithyourwork?工作进行的相当顺利。Theworkisgoingfairlysmoothly.你进步很快。You’remakingrapidprogress.我们想在这里建一座水坝。We’rethinkingofbuildingadamhere.风挺大It’sblowinghard.有人找你接电话。Someoneisaskingforyouonthephone.注意:下面四类动词不宜用现在进行时。(A)表示心理状态、情感的动作:like,love,hate,care,remember,believe,want,mind,wish,agree,mean,need。(B)表存在的状态的动词:appear,exist,lie,remain,seem,belongto,dependon。(C)表示一时性动作的动词:allow,accept,permit,promise,admit,complete。(D)表示感官的动词:see,hear,notice,feel,smell,sound,taste,look。12
现在完成时考点一:for+时间段;since+时间点TheyhavelivedinBeijingforfiveyears.TheyhavelivedinBeijingsince1995.考点二:常见的不确定的时间状语:lately;recently,just,already,yet,ever,never,uptonow;tillnow;sofar,thesedays,once,twice,threetimes… Hasitstoppedrainingyet?考点三:在表示“最近几世纪/年/月以来……”时间状语中,谓语动词用现在完成时。in/over/duringthepastfewyears/months/weeks/days;forthelastfewcenturies,throughcenturies;throughouthistory等考点四:用于现在完成时的句型 ItisthefirsttimethatIhavevisitedthecity. Itwasthethirdtimethattheboyhadbeenlate.1)This/That/Itisthefirst/secondtime….that…结构中的从句部分,用现在完成时。 这是我看过的最好的电影。ThisisthebestfilmthatI"ve(ever)seen. 2)This/That/Itisthebest(worst,mostinteresting,only)+名词+that”后面跟现在完成时。since的四种用法1)since+过去一个时间点 (如具体的年、月、日期、钟点、1980,lastmonth,halfpastsix)。 Ihavebeenheresince1989. 2)since+一段时间+ago Ihavebeenheresincefivemonthsago.3)since+从句 Greatchangeshavetakenplacesinceyouleft. 4)Itis+一段时间+since从句ItistwoyearssinceIbecameapostgraduatestudent.他去过北京。HehasbeentoBeijing.他到北京去了。HehasgonetoBeijing.have/hasbeen…表示曾到过某地(现在回来了)have/hasgone…表示已经到某地去了(现在不在说话处) 12
典型例题(1)---Doyouknowourtownatall? ---No,thisisthefirsttimeI___here.A.was B.havebeen C.came D.amcoming(2)---Haveyou____beentoourtownbefore? ---No,it‘sthefirsttimeI___here.A.even,come B.even,havecome C.ever,come D.ever,havecome注意:非延续性动词的否定形式可以与表示延续时间的状语连用。即动作不发生的状态是可以持续的。(错)Ihavereceivedhisletterforamonth.(对)Ihaven"treceivedhisletterforalmostamonth典型例题1.Youdon‘tneedtodescribeher.I___herseveraltimes. A.hadmet B.havemet C.met D.meet 答案B.首先本题后句强调对现在的影响,我知道她的模样,你不用描述。再次,severaltimes告知为反复发生的动作,因此用现在完成时。2.---I‘msorrytokeepyouwaiting. ---Oh,notatall.I___hereonlyafewminutes.A.havebeen B.hadbeen C.was D.willbe 答案A.等待的动作由过去开始,持续到现在,应用现在完成时。一般过去时的考点分析(考核重点)。①表示过去的事情、动作或状态常与表示过去具体的时间状语连用(或有上下文语境暗示);用于表达过去的习惯;表示说话人原来没有料到、想到或希望的事Imetherinthestreetyesterday.Heusedtosmokealot. Ithoughtthefilmwouldbeinteresting,butitisn’t.Hetoldmehe________aninterestingnovellastnight.②如果从句中有一个过去的时间状语,尽管从句中的动作先于主句发生,但从句中的谓语动词用过去式。③表示两个紧接着发生的动作,常由以下词语连接,如but,and,when,assoonas,immediately,themoment…Themomentshecamein,shetoldmewhathadhappenedtoher.Heboughtawatchbutlostit.12
xTomhaswrittenalettertohisparentslastnight. Tomwrotealettertohisparentslastnight.句子中如有过去时的时间副词(如yesterday,last,week,in1960)时,不能使用现在完成时,要用过去时。过去进行时表示过去某个时间点或某段时间内正在发生的动作。Theboywasdoinghishomeworkwhenhisfathercamebackfromwork.Whatwereyoudoingatninelastnight?Theradio_wasbeingrepaired_whenyoucalledme.----whatwereyoudoingthistimeyesterday?----Wewereworkinginthelab.过去完成时考点分析(考核重点)句中有明显的参照动作或时间状语,这种时态从来不孤立使用(by、bytheend、bythetime、until、before、since后接表示过去某一时间的短语或从句以前发生的动作。E.G:Bytheendoflastyear,wehadproduced20,000cars.Thetrainhadleftbeforewereachedthestation.Itwasthreeyearssincewehadbeenthere.考点一:表示“一……就”的几个句型:Hardly/Scarcely/Nosoonerhad+主语+过去分词+when/before/than+一般过去时 Wehadnosoonerbeenseatedthanthebusstarted.=Nosoonerhadwebeenseatedthanthebusstarted.(注意主谓倒装)考点二:表示“第几次做某事”,主句用过去时,从句用过去完成时。Thatwasthesecondtimethatshehadseenhergrandfather.Itwas3yearssincewehadparted。考点三:表示未曾实现的希望、打算、意图、诺言等。常用hadhoped/planned/meant/intended/thought/wanted/expected等或用上述动词过去式接不定式完成式表示即:hoped/planned…+tohavedone。IhadhopedthatIcoulddothejob.IhadintendedtoseeyoubutIwastoobusy.12
考点四:“时间名词+before”在句子中作状语,用于间接引语中谓语动词用过去完成时;“时间名词+ago”在句中作状语,谓语动词用一般过去式。Hesaidhisparentshaddiedtenyearsbefore.XiaoHualeftschool3yearsago.典型例题: Thestudents___busilywhenMissBrownwenttogetabookshe___intheoffice. A.hadwritten,left B.werewriting,hasleft C.hadwritten,hadleftD.werewriting,hadleft一般将来时考点分析①表示一种趋向或习惯动作。We’lldiewithoutairorwater.②begoingto与will/shall,betodo,beabouttodo用法及区别:begoingto表示现在打算在最近或将来要做某事,这种打算往往经过事先考虑,甚至已做了某种准备;shall/willdo表示未事先考虑过,即说话时临时作出的决定。Ifitisfine,we’llgofishing. Ifitisfine,wearegoingtogofishing. 注意:begoingto表将来,不能用在条件状语从句的主句中;而will则能betodosth.表按计划、安排即将发生的动作/不可避免地将要发生的事,命中注定的事。Ameetingistobeheldat3:00o’clocktomorrow.beabouttodosth.表示“正打算,就要”Autumnharvestisabouttostart.w:“祈使句+and/or+句子”,这种结构中and后面的句子谓语用一般将来时。 Useyourheadandyouwillfindaway.将来进行时表将来某个时间正在发生的动作,或按计划一定会发生的事情。明天这会我正在写作业。I’llbedoingmyhomeworkthistimetomorrow. 将来完成时表在将来某时刻之前业已完成的事情,时间状语非常明显。考点一:常用的时间状语一般用by+将来的时间。Bytheendofnextmonth,hewillhavetraveled1000milesonfoot.Bythetimeyoureachthestation,thetrain______.考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,将来完成时则由现在完成时表示。Thechildrenwilldotheirhomeworkthemomenttheyhavearrivedbackfromschool.12
一般过去时和过去完成的用法区别1.一般过去时是对现在说话时刻而言的,过去完成时则是对过去某一时刻而言.两种时态2.建立的时间参照点不同,对过去完成时来说,这一个时间参照点十分重要,它是过去完成3.概念赖以建立的基础,也是和一般过去时相区别的重要标准.2.过去完成时的时间状语常用by和before引导的短语表示,如bythattime,bytheendof….,before2000,bythetime+句子等.过去完成时和现在完成时的区别1.两种时态都常与一段时间和状语连用,但现在完成时表示的是延续到现在或同现在有关的动作(句中不可有表示过去特定时间的状语),而过去完成时表示的是在过去某时之前已经完成或延续到过去某时的动作(句中有表示过去特定时间的状语).2.比较下面的说法Shehadbeenillforaweekbeforeshecameback.她在回来之前就生病一个星期了.(回来发生在过去某一时间,发病发生在过去的过去)Shehasbeenillforaweek.她生病一个星期了.(现在仍在生病)考点一:不能用于被动语态的动词和词组 cometrue,consistof,takeplace,happen,become,rise,occur,belongto,breakout,appear,arrive,die,fall,last,exist,fail,succeedIttookplacebeforeliberation.考点二:下列动词的主动语态表示被动意义,而且常与well,quite,easily,badly等副词连用。 ulock(锁);wash(洗);sell(卖);read(读);wear(穿);write(写);break(破碎)Glassbreakseasily.玻璃容易破碎。Thedoorwon’tlock.门锁不上。Thebooksellswell.这本书很畅销。v当feel,look,smell,taste,sound等后面接形容词时;用主动表示被动含义③want,require,need后面的动名词用主动表示被动含义。④beworthdoing用主动形式表示被动含义。⑤在“be+形容词+todo”中,不定式的逻辑宾语是句子的主语,用主动代被动。Thiskindofwaterisn’tfittodrink.Thegirlisn’teasyto_getalongwith.另外:betoblame(受谴责),betorent/let(出租)也用主动形式表被动。12
4)被动形式表示主动意义的几种情况。①beseated坐着Heisseatedonabench.(Heseatshimselfonabench.)②behidden躲藏Hewashiddenbehindthedoor.(Hehidhimselfbehindthedoor.)他藏在门后。③belost迷路④bedrunk喝醉⑤bedressed穿着Thegirlwasdressedinaredshortskirt.考点三:一些常用经典被动句型:Itissaid…,Itisreported…,Itiswidelybelieved…,Itisexpected…,Itisestimated…,这些句子一般翻译为“据说……”,“人们认为……”,而“以前人们认为……”则应该说:Itwasbelieved…,Itwasthought…高考时态题精练1.----myglasses?---Yes,Isawthemonyourbedaminuteago.A.DoyouseeB.HadyouseenC.WouldyouseeD.Haveyouseen2.Helenherkeysintheofficesoshehadtowaituntilherhusbandhome.A.Hasleft/comesB.left/hadcomeC.hadleft/cameD.hadleft/wouldcome.3.----CanIhelpyou,sir?-----Yes,Iboughtthisradiohereyesterday,butit________A.didn’tworkB.won’tworkC.can’tworkD.doesn’twork4.IfirstmetLisathreeyearsago.Sheataradioshopatthetime.A,hasworkedB.wasworkingC.hadbeenworkingD.hadworked5.WhoisJerryCooper??Isawyoushakinghandswithhimatthemeeting.A.Don’tyoumeethimyetB.Hadn’tyoumethimyetC.Didn’tyoumeethimyetD.Haven’tyoumethimyet6.ShirleyabookaboutChinalastyearbutIdon’tknowwhethershehasfinishedit.A.haswrittenB.wroteC.hadwrittenD.waswriting7.-----Hi,Tracy.Youlooktired.------Iamtired.Ithelivingroomallday.A.paintedB.hadpaintedC.havebeenpaintingD.havepainted12
7.Theprice,butIdoubtwhetheritwillremainso.A.wentdownB.willgodownC.hasgonedownD.wasgoingdown8.Iping_pongquitewell,butIhaven’thadtimetoplaysincethenewyear.A.WillplayB.haveplayedC.playedD.play9.----Nancyisnotcomingtonight.-----Butshe.A.promiseB.promisedC.willpromisedD.hadpromised10.----Alice,whydidn’tyoucomeyesterday?-----I,butIhadanunexpectedvisitor.A.hadB.wouldC.wasgoingtoD.did11.----Hey,lookwhereyouaregoing!----Oh,I’mterriblesorry..A.I’mnotnoticingB.Iwasn’tnoticingC.Ihaven’tnoticedD.Idon’tnotice12.----You’veleftthelighton.----Oh,soIhave.andturnit.A.I’llgoB.I’vegoneC.IgoD.I’mgoing13.-----Howareyoutoday?-----Oh,IasillasIdonowforaverylongtime.A.didn’tfeelB.wasn’tfeelingC.don’tfeelD.haven’tfelt14.ThereportersaidthattheUFOeasttowestwhenhesawit.A.wastravellingB.travelledC.hadbeentravellingD.wastotravel15.Selectingamobilephoneforpersonaluseisaneasytaskbecausetechnologysorapidly.A.ischangingB.haschangedC.willhavechangedD.willchange16.Visitorsnottotouchtheexhibits.A.willrequestB.requestC.arerequestingD.arerequested17.-----Excuseme,sir.Wouldyoudomeafavor?-----Ofcourse.Whatisit?-----Iifyoucouldtellmehowtofilloutthisform.A.hadwonderedB.waswonderingC.wouldwonderingD.didwonder18.IwonderwhyJenny_____usrecently.Weshouldhaveheardfromherbynow.12
A.hasn"twrittenB.doesn"twriteC.won"twriteD.hadn"twritten19.Idon"treallyworkhere.I______untilthenewsecretaryarrives.A.justhelpoutB.havejusthelpedoutC.amjusthelpingoutD.willjusthelpout【解析】“我只是在帮忙,直到新秘书到任为止”20.HewillhavelearnedEnglishforeightyearsbythetimehe_________fromtheuniversitynextyear.A.willgraduateB.willhavegraduateC.graduatesD.istograduate【解析】bythetime后接定语从句,省略了关系副词when。在这种定语从句中要用一般现在时表示将来。英语动词时态、语态考点误用1.对不起,我没看见你在这儿。 [误]Sorry,Idon"tseeyouhere.[正]Sorry,Ididn‘tseeyouhere. [析]根据语境,本句是指刚才没看见对方在这,而不是现在没看见对方在这,所以要用一般过去时。 2.你能告诉我北京冬天是否下雪吗? [误]CouldyoutellmeifitsnowedinwinterinBeijing?[正]CouldyoutellmeifitsnowsinwinterinBeijing?[析]一般现在时除表示经常性的动作外,还可表示习惯性的动作,即现阶段的一个事实,句中不需要任何经常性的时间状语配合。could表示一种客气的语气,不表示过去时态。3.他说他第二天要去合肥出差。 [误]HesaidhewillgotoHefeionbusinessthenextday. [正]HesaidhewouldgotoHefeionbusinessthenextday. [析]主句谓语动词为过去时,宾语从句表示过去的将来要发生的动作,要用过去将来时。 4.我忘了把你的伞带来了。 [误]Iforgettobringyourumbrellawithme. [正]Iforgottobringyourumbrellawithme. [析]不用forget,而用forgot,因为现在已经记起来了,forgot是说话这一时刻之前的动作。由于受汉语思维习惯的影响,动词时态观念不强,误把一般现在时当作一般过去时。5.他父亲离开祖国已经50年了。 [误]Hisfatherhaslefthishomelandforfiftyyears. [正]Hisfatherhasbeenawayfromhishomelandforfiftyyears. [析]短暂性动词的完成时(肯定式)不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,要么改为表示状态的动词,要么用下列句式来表达(以此句为例): Hisfatherlefthishomelandfiftyyearsago. Itisfiftyyearssincehisfatherlefthishomeland. Ithasbeenfiftyyearssincehisfatherlefthishomeland. 12
Fiftyyearshavepassedsincehisfatherlefthishomeland. 6.“你去过北京吗?”“是的,我去过。” [误]“HaveyougonetoBeijing?”“Yes,Ihavegonethere.” [正]“HaveyoubeentoBeijing?”“Yes,Ihavebeenthere.” [析]HaveyougonetoBeijing?是“你已经到北京了吗?”,指目前人已在北京或在赴北京的途中。说话的时候,显然你已不在北京了,所以说用在这儿不恰当。表示“过去曾去过某处而现在又回来了”须用havebeen。 7.如果明天不下雨,我们就去参观美术展览。 [误]Weshallseeanexhibitionofpain-tingsifitwon“traintomorrow. [正]Weshallseeanexhibitionofpain-tingsifitdoesn”traintomorrow. [析]在时间状语从句中,从句要用一般现在时表示将来的动作。8.在过去几年中,我们家乡发生了巨大的变化。 [误]Thereweregreatchangesinourhome-towninthepastfewyears. [正]Therehavebeengreatchangesinourhometowninthepastfewyears. [析]“In/Duringthepast/last+复数名词”是完成时态的标志之一,不要被past/last所迷惑,而用了过去时。 9.我不知道那艘船明天是否会准点到。 [误]Iwonderiftheshiparrivesontimetomorrow. [正]Iwonderiftheshipwillarriveontimetomorrow. [析]这里if连接的宾语从句,表示“是否”(=whether),而不是条件状语从句,表示“如果”。因此根据句意仍需用一般将来时。10.自从1978年以来我们的家乡发生了巨大的变化。 [误]Greatchangeshavebeentakenplaceinourhometownsince1978. [正]Greatchangeshavetakenplaceinourhometownsince1978. [析]takeplace和happen都是不及物动词或短语,不能用于被动语态。 11.那个村也叫国际会议村。 [误]ThevillagealsocalledtheInternationalMeetingVillage. [正]ThevillageisalsocalledtheInternationalMeetingVillage. [析]英语被动语态是由“be+动词的过去分词”构成,因此在also前应加is。 12.我们学校也教俄语。 [误]OurschoolalsoteachesRussian. [正]Russianisalsotaughtinourschool. [析]当动作的执行者没有必要指明或为大家所知时,通常用被动语态。显然ourschool不是teach的执行者,而应该是没有表示出来的teachers,因此,要把动作的承受者Russian用作主语,用被动语态来表达。 13.我们都认识那位科学家。 [误]Thescientistisknownbyusall. [正]Thescientistisknowntousall. [析]by表示动作执行者。而表示范围、地点等用法时,要用介词to或in。 14.孩子们陆续地走进了博物馆。 12
[误]Themuseumwasenteredbythechildrenonebyone. [正]Thechildrenenteredthemuseumonebyone. [析]某些及物动词,如leave,enter,reach,join等后接表示地点、处所、组织名称的名词作宾语时,不能转换为被动语态。 15.他在会上向我们作了自我介绍。 [误]Himselfwasintroducedtousatthemeetingbyhim. [正]Heintroducedhimselftousatthemeeting. [析]反身代词作宾语时,不能转换成被动语态。 16.这本杂志在这儿很畅销。 [误]Thismagazineissoldwellhere. [正]Thismagazinesellswellhere. [析]有些动词,如:act,add,brush,burn,clean,cook,count,cut,draw,drive,keep,lock,look,open,read,sell,smoke,strike,wash,wear,write等,其主动形式在一些具体场合表示被动意义。这类句子的特点是:主语往往是"物"而不是"人"。另外,后面往往带有well这一类副词,或者修饰主语的形容词12